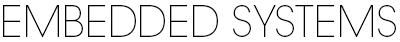Sequential PLEX, and its Potential for Parallel Execution
Publication Type:
Conference/Workshop Paper
Venue:
13th International Workshop on Compilers for Parallel Computers, CPC 2007
Abstract
Some computer systems have been designed under the assumption
that activities in the system are executed non-preemptively.
Exclusive access to any shared data in such a system is automatically
guaranteed as long as the system is executed on a single-processor architecture.
However, if the activities are executed on a multiprocessor,
exclusive access to the data must be guaranteed when memory conflicts
are possible. An analysis of the potential memory conflicts can be
used to estimate the possibility for parallel execution.
Central parts of the AXE telephone exchange system from Ericsson is
programmed in the language PLEX. The current software is executed
on a single-processor architecture, and assumes non-preemptive execution.
In this paper, we investigate some existing PLEX code with respect to
the number of possible shared-memory conflicts that could arise if the
existing code, without modifications, would be executed on a parallel
architecture. Our initial results are promising; only by examining the
data that actually can be shared, we manage to reduce the number
of conflicts from the assumed 100% to figures between 25-75% for the
observed programs. Simple optimizations decrease the numbers even
further.
Bibtex
@inproceedings{Lindhult1128,
author = {Johan Lindhult and Bj{\"o}rn Lisper},
title = {Sequential PLEX, and its Potential for Parallel Execution},
month = {July},
year = {2007},
booktitle = {13th International Workshop on Compilers for Parallel Computers, CPC 2007},
url = {http://www.es.mdu.se/publications/1128-}
}